Cryptologists are professionals who specialize in the study of cryptography and cryptanalysis. They use mathematical algorithms and computer systems to develop and decipher codes that protect sensitive information, such as financial transactions, military communications, and government secrets. Cryptology is a complex field that requires a strong background in mathematics, computer science, and engineering, as well as a deep understanding of security protocols and data protection laws.
The role of a cryptologist is multifaceted and can vary depending on the industry and employer. Some cryptologists work for government agencies, such as the National Security Agency (NSA) or the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), where they are responsible for developing and breaking codes used in military and intelligence operations. Others work for private companies, such as financial institutions or technology firms, where they develop and implement security measures to protect sensitive data from cyber attacks.
Key Takeaways
- Cryptologists are experts in cryptography and cryptanalysis, using mathematical algorithms and computer systems to develop and decipher codes that protect sensitive information.
- The role of a cryptologist can vary depending on the industry and employer, with some working for government agencies and others working for private companies.
- Cryptology is a complex field that requires a strong background in mathematics, computer science, and engineering, as well as a deep understanding of security protocols and data protection laws.
Fundamentals of Cryptology
Cryptology is the science of secure communication and data storage. It involves the use of mathematical algorithms and cryptographic techniques to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Cryptology has a long history, dating back to ancient times when people used simple encryption methods to protect their messages. Today, cryptology is a complex and sophisticated field that plays a crucial role in modern information security.
History of Cryptography
The history of cryptography can be traced back to the ancient Greeks, who used simple substitution ciphers to protect their messages. Over time, cryptography evolved and became more complex. During World War II, cryptography played a critical role in the war effort, with codebreakers working to decipher enemy messages. Today, cryptography is used in a wide range of applications, from securing online transactions to protecting military communications.
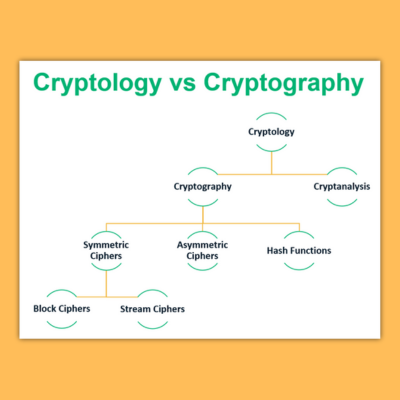
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This means that the key must be kept secret to prevent unauthorized access. Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This allows for secure communication without the need to share a secret key.
Cryptographic Algorithms
There are many different cryptographic algorithms used in modern cryptology. These algorithms are designed to be secure and resistant to attacks. Some of the most common cryptographic algorithms include AES, RSA, and SHA. AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm used to protect sensitive data, while RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm used for secure communication. SHA is a hashing algorithm used to verify the integrity of data.
Overall, cryptology is a complex and important field that plays a critical role in modern information security. By using mathematical algorithms and cryptographic techniques, cryptologists are able to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensure the privacy and security of online communication.

Roles and Responsibilities of a Cryptologist
Cryptologists play a critical role in ensuring the security of sensitive information by developing and implementing encryption methods. They are responsible for both creating and breaking codes, and often work with complex mathematical formulas and algorithms.
Code Making
One of the primary responsibilities of a cryptologist is to create codes that can be used to protect sensitive information. This involves developing encryption methods that can be used to scramble data in a way that only authorized parties can access it. Cryptologists may work with a variety of encryption methods, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption, and must be able to adapt their methods to suit the needs of their clients.
Code Breaking
In addition to creating codes, cryptologists must also be able to break them in order to access sensitive information that has been encrypted by others. This requires a deep understanding of cryptanalysis methods, as well as a knowledge of the latest encryption technologies. Cryptologists may use a variety of techniques to break codes, including statistical analysis, frequency analysis, and brute force methods.
Cryptanalysis Methods
Cryptanalysis is the process of analyzing encrypted data in order to understand its underlying structure and break the code. There are a variety of cryptanalysis methods that cryptologists may use, including:
- Frequency Analysis: This involves analyzing the frequency of letters or characters in a message in order to identify patterns that can be used to break the code.
- Statistical Analysis: This involves using statistical methods to analyze encrypted data in order to identify patterns and relationships that can be used to break the code.
- Brute Force Methods: This involves trying every possible combination of letters or characters until the code is broken.
Overall, the role of a cryptologist is critical in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. By creating and breaking codes, and using a variety of cryptanalysis methods, cryptologists play a vital role in ensuring the security of our digital world.
Applications of Cryptography
Cryptography is a technique that involves converting plain text into a coded message to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Cryptologists use cryptography to secure digital communications, safeguard financial transactions, and protect sensitive data. Cryptography has a wide range of applications in various fields, including digital security, communication systems, and cryptocurrencies.
Digital Security
Cryptography plays a critical role in digital security by protecting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal data. Cryptography is used to encrypt data stored on computers, mobile devices, and servers to prevent unauthorized access. Cryptographic techniques such as hashing and digital signatures are used to verify the integrity of data and ensure that it has not been tampered with.
Communication Systems
Cryptography is used to secure communication systems such as email, messaging apps, and voice over IP (VoIP) services. Cryptographic protocols such as SSL/TLS are used to encrypt data transmitted over the internet to prevent eavesdropping and data theft. Cryptography is also used to secure wireless networks and mobile communication systems.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum use cryptography to secure transactions and protect user privacy. Cryptographic techniques such as public-key cryptography and digital signatures are used to verify transactions and prevent double-spending. Cryptography is also used to protect the anonymity of users and prevent the tracing of transactions.
In conclusion, Cryptography is a vital tool for securing digital communications, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring the integrity of financial transactions. Cryptologists use cryptography to safeguard information in various fields, including digital security, communication systems, and cryptocurrencies.

Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifications are necessary to become a cryptologist?
To become a cryptologist, one must have a strong background in mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. A bachelor’s degree in a related field is typically required, with many employers preferring a master’s degree. In addition, experience with cryptography and encryption technologies is highly valued.
What is the typical job description for a cryptologist?
Cryptologists are responsible for analyzing and interpreting data and patterns to decipher and generate encoded signals. They work to establish secure channels of communication and ensure that sensitive information is protected. Cryptologists may also work to develop new encryption methods and technologies.
How do cryptologist salaries compare within government and private sectors?
Salaries for cryptologists can vary depending on the industry and location. In general, cryptologists working in the government or military can expect to earn a higher salary than those working in the private sector. However, salaries can also vary depending on the level of experience and education of the cryptologist.
What roles do cryptologists play in the Navy or other military branches?
Cryptologists play a critical role in the Navy and other military branches. They are responsible for protecting sensitive information and ensuring that communications remain secure. Cryptologists may also work to develop new encryption technologies and methods.
What career opportunities exist for cryptologists?
Cryptologists may find employment in a variety of industries, including government, military, and private sector. Some common job titles for cryptologists include Cryptologic Technician, Cryptologic Officer, and Cryptography Analyst. Cryptologists may also work in research and development, developing new encryption technologies and methods.
How does the role of a cryptologist differ from that of a cryptographer?
While the terms “cryptologist” and “cryptographer” are often used interchangeably, there are some key differences between the two roles. Cryptographers are responsible for creating and cracking encryption algorithms, while cryptologists are responsible for analyzing and interpreting data and patterns to decipher and generate encoded signals. Cryptographers may also work to develop new encryption technologies and methods, while cryptologists may work to establish secure channels of communication and protect sensitive information.